Many people create SEO oriented texts when creating profitable websites. Well, yes, everybody needs traffic. And with the widespread implementation of AI, it became a panacea for some time. But a while back, Google decided to take control of all this and released another core update which affected a lot of websites including those used as donors for link building.
The update was received ambiguously: there are those who benefited from it, primarily sites with a very narrow thematic focus. At the same time, there is a significant amount of projects which were seriously affected by it. Some people say it’s a collapse of the business for a number of independent webmasters. For example, the traffic and revenue of sites like retrododo.com and housefresh.com have decreased by more than 85%, putting the business on the brink of collapse.
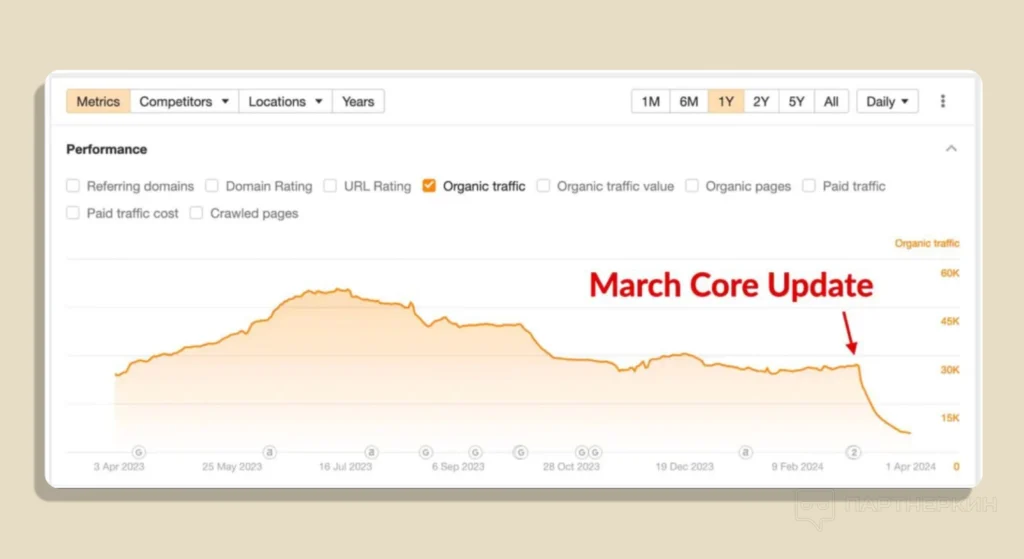
What’s new in this update? We have gathered opinions from SEO specialists to show which solutions can help you maintain your traffic if it has dropped after these updates.
What Does Google Want?
The main task, as before, is to improve the quality of search results. Google aims to “eliminate” useless content. To achieve this, they have implemented new spam policies targeting the prevention of three common methods:
Misuse of Old Domains
This refers to the purchase of old domains to place content aimed at SEO traffic. Webmasters rely on search engines to rank such sites highly due to the previous authority of the domains.
For example, purchasing the domain of a former medical site and filling it with meaningless texts about casinos. The search engine identifies and penalizes such sites. However, there is a chance to remove Google block from it.
At the same time, buying drop domains is allowed provided that the websites created contain useful content for users.
Mass Creation of Useless Content
This refers to websites that produce a huge amount of similar texts with the aim of improving their rankings in search engines even if they have keywords in URLs. Here, it does not matter who the author of the material is: whether it is a human or AI.
Google already had rules against automated spam. Now, the policy has been tightened, and any useless material for manipulating search engines is prohibited.
Abuse of Website Reputation or “Parasitic” SEO
This occurs when third-party content is placed on an authoritative website, such as advertisements, partnership materials, and other content without proper control. Webmasters try to bypass the search engine and increase the visibility of the resource in search results.
The fact of placing third-party content is not prohibited. Many sites publish advertising materials; this is normal practice if it is done transparently for the audience.
The problem arises when such content is placed uncontrollably, without benefit to users. The main goal here is manipulating search results using the authority of the original site.
Google intends to actively find and eliminate such violations. Websites found to contain spam will be downgraded in search results or excluded from them.
What Do Webmasters Say?
Quick penalties:
The new Google update imposes penalties on violating sites almost instantly. This has caused a wave of concern among webmasters who do not understand why their sites have disappeared from search results.
SEO expert Lily Ray mentioned on “X” that more than a dozen sites suddenly disappeared within a day.
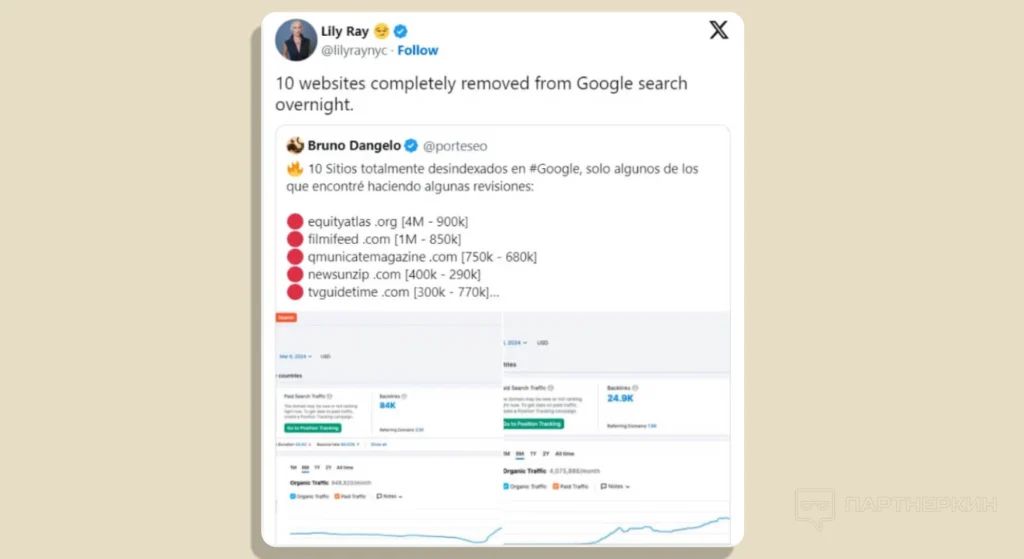
It’s important that Google no longer notifies site owners about sanctions through Google Search Console.
Complete de-indexing of the entire site:
Webmasters were most afraid of complete removal of sites from the index. This affects resources with low-quality or irrelevant content.
SEO expert Jeff Coyle notes on “X”:
“I have been tracking search results for a group of spam sites that have been slowly rising over the past year. Many of them have been completely removed, while others have significantly dropped.”

Impact on small sites with AI content:
The update also affected small sites that actively use AI to create content. The algorithm better identifies such content and lowers its positions in search results.
SEO expert Craig Griffiths believes that the frequency of publications is one of the main indicators of AI content.
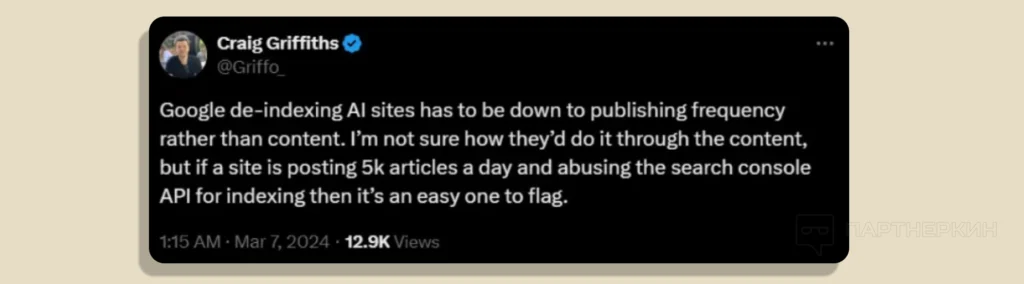
Google’s goal is not to fight all AI content but to exclude useless and repetitive materials from search results, regardless of whether they were created by a human or a program.
This update is intended to cleanse search results of spammy and unnecessary sites, promoting high-quality resources to the top.
Useful content affected:
Other SEO experts, Taleb Kabbara and Alec Griffiths, discovered algorithms that search for duplicated content. For example, Alec reviews camera lenses, their accessories, and describes benchmarks for memory cards on one of his sites.
After auditing the site, he found that he had duplicate data in tables — duplication and keyword over-optimization. The site used templates to create numerous pages for different camera models and accessories, and some content was repeated from page to page.
The benchmarks for memory cards were particularly affected since they often use the same data in different sections.
After auditing the site, Alec removed duplicate pages from the index to see how much it would impact traffic.
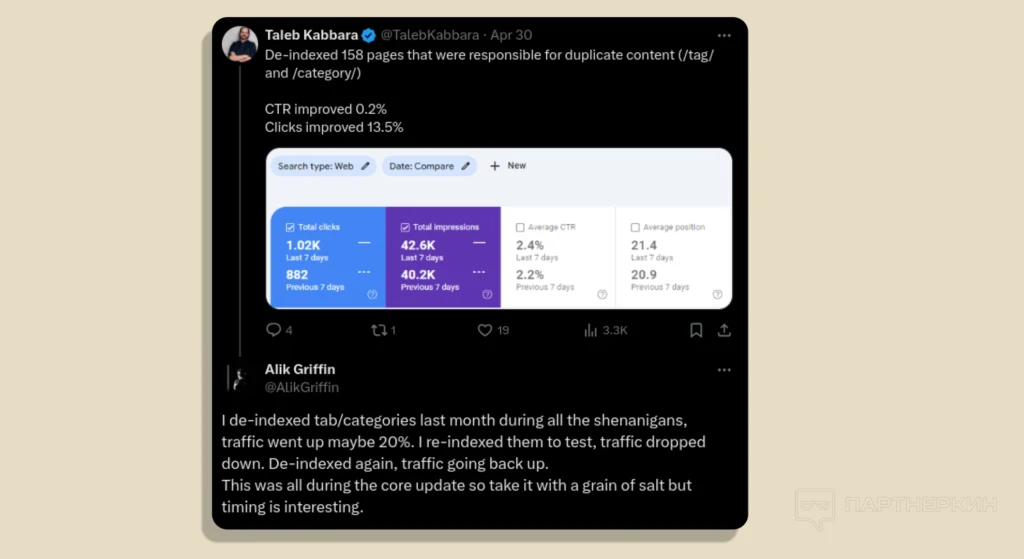
Results:
- Initial De-indexing: Traffic increased by 20%;
- Re-indexing: When he added these pages back to the index, traffic dropped again;
- Re-de-indexing: After de-indexing the pages again, traffic rose once more.
Unfortunately, it appears that the algorithms penalize sites even for unintentional duplication of content.
“I rebuilt all my tables, reducing the amount of duplicate data, and reorganized them to repeat less often,” continues Alec Griffiths. This significantly helped reduce the negative impact of duplication.
Conclusion: How to Save SEO Traffic?
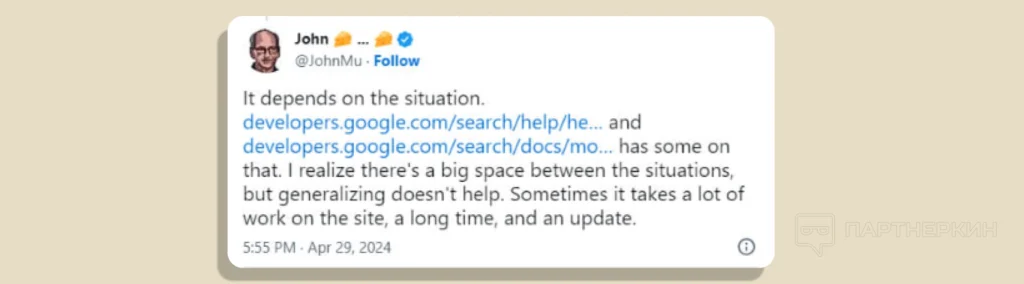
Site owners and SEO specialists have long awaited clarification from Google on how to regain positions after algorithm changes. John Mueller, a Google search specialist, provided his comments. In his assessment, position recovery can take a long time. In some cases, it may take several months, and resolving serious issues will require the next algorithm update.